In a startling discovery that raises fundamental questions about human behavior, researchers at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have determined that the immune system directly affects – and even controls – creatures’ social behavior, such as their desire to interact with others.
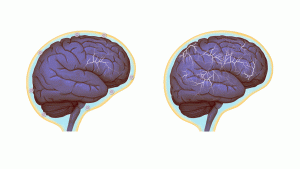
Normal brain activity, left, and a hyper-connected brain. (Images by Anita Impagliazzo, UVA Health System)
So could immune system problems contribute to an inability to have normal social interactions? The answer appears to be yes, and that finding could have significant implications for neurological diseases such as autism-spectrum disorders and schizophrenia.
“The brain and the adaptive immune system were thought to be isolated from each other, and any immune activity in the brain was perceived as sign of a pathology. And now, not only are we showing that they are closely interacting, but some of our behavior traits might have evolved because of our immune response to pathogens,” explained Jonathan Kipnis, chair of UVA’s Department of Neuroscience. “It’s crazy, but maybe we are just multicellular battlefields for two ancient forces: pathogens and the immune system. Part of our personality may actually be dictated by the immune system.”
Evolutionary Forces at Work
It was only last year that Kipnis, the director of UVA’s Center for Brain Immunology and Glia, and his team discovered that meningeal vessels directly link the brain with the lymphatic system. That overturned decades of textbook teaching that the brain was “immune privileged,” lacking a direct connection to the immune system. The discovery opened the door for entirely new ways of thinking about how the brain and the immune system interact.
The follow-up finding is equally illuminating, shedding light on both the workings of the brain and on evolution itself. The relationship between people and pathogens, the researchers suggest, could have directly affected the development of our social behavior, allowing us to engage in the social interactions necessary for the survival of the species while developing ways for our immune systems to protect us from the diseases that accompany those interactions. Social behavior is, of course, in the interest of pathogens, as it allows them to spread.
The UVA researchers have shown that a specific immune molecule, interferon gamma, seems to be critical for social behavior and that a variety of creatures, such as flies, zebrafish, mice and rats, activate interferon gamma responses when they are social. Normally, this molecule is produced by the immune system in response to bacteria, viruses or parasites. Blocking the molecule in mice using genetic modification made regions of the brain hyperactive, causing the mice to become less social. Restoring the molecule restored the brain connectivity and behavior to normal. In a paper outlining their findings, the researchers note the immune molecule plays a “profound role in maintaining proper social function.”
“It’s extremely critical for an organism to be social for the survival of the species. It’s important for foraging, sexual reproduction, gathering, hunting,” said Anthony J. Filiano, Hartwell postdoctoral fellow in the Kipnis lab and lead author of the study. “So the hypothesis is that when organisms come together, you have a higher propensity to spread infection. So you need to be social, but [in doing so] you have a higher chance of spreading pathogens. The idea is that interferon gamma, in evolution, has been used as a more efficient way to both boost social behavior while boosting an anti-pathogen response.”












